Understanding Global Markets and GDP: A Comprehensive Overview

In today’s interconnected world, the dynamics of the global market and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) are pivotal in shaping economies, influencing trade policies, and guiding investment decisions. This blog aims to unpack these concepts, explore their interrelationship, and provide insights into their impact on global economic stability and growth.
Global Market Dynamics
1. What is the Global Market?
The global market refers to the international exchange of goods, services, and capital between countries. It encompasses various sectors, including finance, trade, and investment. This market is driven by the need for countries to access resources not available domestically, seek new investment opportunities, and expand their economic influence.
2. Key Drivers of the Global Market
- Trade Agreements: Agreements like the USMCA or EU trade deals facilitate smoother transactions and reduce tariffs, fostering greater economic cooperation.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in technology enable more efficient production, logistics, and communication, thus enhancing global trade capabilities.
- Economic Policies: Monetary and fiscal policies of major economies influence global trade patterns and investment flows.
- Geopolitical Events: Political stability, conflicts, and diplomatic relations can significantly impact market confidence and economic activities.
3. Trends Shaping the Global Market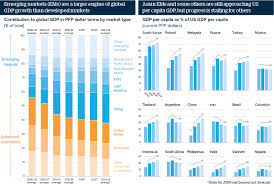
- Globalization: The integration of economies has accelerated, leading to increased international trade and investment flows.
- Digital Transformation: E-commerce, digital currencies, and fintech innovations are reshaping traditional business models and market dynamics.
- Sustainability: There is a growing emphasis on sustainable practices, impacting everything from investment strategies to consumer behavior.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
1. What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total economic output of a country within a specific period, typically a year. It reflects the value of all goods and services produced and serves as a key indicator of economic health. GDP can be calculated using three approaches: production, income, and expenditure.
2. Components of GDP
- Consumption: The total value of goods and services consumed by households.
- Investment: Expenditures on capital goods that will be used for future production, including business investments in equipment and infrastructure.
- Government Spending: Total government expenditures on goods and services.
- Net Exports: The value of exports minus imports. A positive value indicates a trade surplus, while a negative value indicates a trade deficit.
3. GDP Growth and Economic Indicators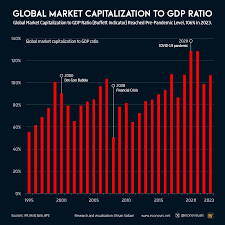
GDP growth rate is a critical indicator of economic performance. High growth suggests a robust economy, while low or negative growth might signal economic trouble. Analysts also consider other indicators like unemployment rates, inflation, and consumer confidence to gauge economic health.
The Interplay Between Global Markets and GDP
1. Impact of Global Markets on GDP
Global market conditions can significantly influence a country’s GDP. For instance, a global economic downturn can reduce demand for exports, impacting the GDP of exporting countries. Conversely, robust global market growth can stimulate investment and trade, boosting GDP.
2. The Role of GDP in Shaping Global Markets
Countries with strong and growing GDPs often attract more foreign investment and participate more actively in global trade. High GDP can also enhance a country’s negotiating power in international trade agreements and economic forums.
3. Case Studies
- China’s Rise: China’s rapid economic growth has made it a major player in the global market, influencing global trade patterns and investment flows.
- The Eurozone Crisis: Economic challenges in the Eurozone affected global markets, demonstrating the interconnectedness of economies.
Conclusion
Understanding global markets and GDP is essential for grasping the complexities of the modern economy. While GDP provides a snapshot of a country’s economic performance, global market dynamics offer a broader view of how economies interact and influence one another. Staying informed about these factors can help investors, policymakers, and businesses navigate the ever-evolving economic landscape and make informed decisions.
As the global economy continues to evolve, keeping an eye on these metrics will be crucial for predicting trends, understanding market movements, and preparing for future economic shifts.

 Businesses and investors need to stay agile and adaptable to the evolving global market landscape. This may involve diversifying investments, exploring new markets, and leveraging technological advancements. Adapting to changing economic conditions and trade policies will be key to maintaining competitiveness.2. Risk ManagementEffective risk management strategies are crucial in navigating uncertainties in global markets. Businesses should assess potential risks, including geopolitical, economic, and environmental factors, and develop contingency plans to mitigate their impact.3. Sustainable PracticesEmbracing sustainability can provide long-term benefits for businesses and economies. Companies investing in green technologies and sustainable practices may not only comply with regulatory requirements but also attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors.4. Informed Decision-MakingStaying informed about global market trends and economic indicators will enhance decision-making capabilities. Businesses and investors should regularly analyze market data, economic forecasts, and policy changes to make well-informed strategic choices.ConclusionThe relationship between global markets and GDP is complex and dynamic, influenced by a multitude of factors ranging from technological advancements to geopolitical events. As we move forward, understanding these interactions will be crucial for navigating the global economic landscape.By keeping abreast of emerging trends, adapting to changes, and employing effective risk management strategies, businesses and investors can better position themselves for success in an ever-evolving global market. The future will undoubtedly bring both challenges and opportunities, and those who stay informed and adaptable will be best equipped to thrive in this interconnected
Businesses and investors need to stay agile and adaptable to the evolving global market landscape. This may involve diversifying investments, exploring new markets, and leveraging technological advancements. Adapting to changing economic conditions and trade policies will be key to maintaining competitiveness.2. Risk ManagementEffective risk management strategies are crucial in navigating uncertainties in global markets. Businesses should assess potential risks, including geopolitical, economic, and environmental factors, and develop contingency plans to mitigate their impact.3. Sustainable PracticesEmbracing sustainability can provide long-term benefits for businesses and economies. Companies investing in green technologies and sustainable practices may not only comply with regulatory requirements but also attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors.4. Informed Decision-MakingStaying informed about global market trends and economic indicators will enhance decision-making capabilities. Businesses and investors should regularly analyze market data, economic forecasts, and policy changes to make well-informed strategic choices.ConclusionThe relationship between global markets and GDP is complex and dynamic, influenced by a multitude of factors ranging from technological advancements to geopolitical events. As we move forward, understanding these interactions will be crucial for navigating the global economic landscape.By keeping abreast of emerging trends, adapting to changes, and employing effective risk management strategies, businesses and investors can better position themselves for success in an ever-evolving global market. The future will undoubtedly bring both challenges and opportunities, and those who stay informed and adaptable will be best equipped to thrive in this interconnected